The Rise of AR Smart Glasses: Advancing Interactivity and Transforming Industries
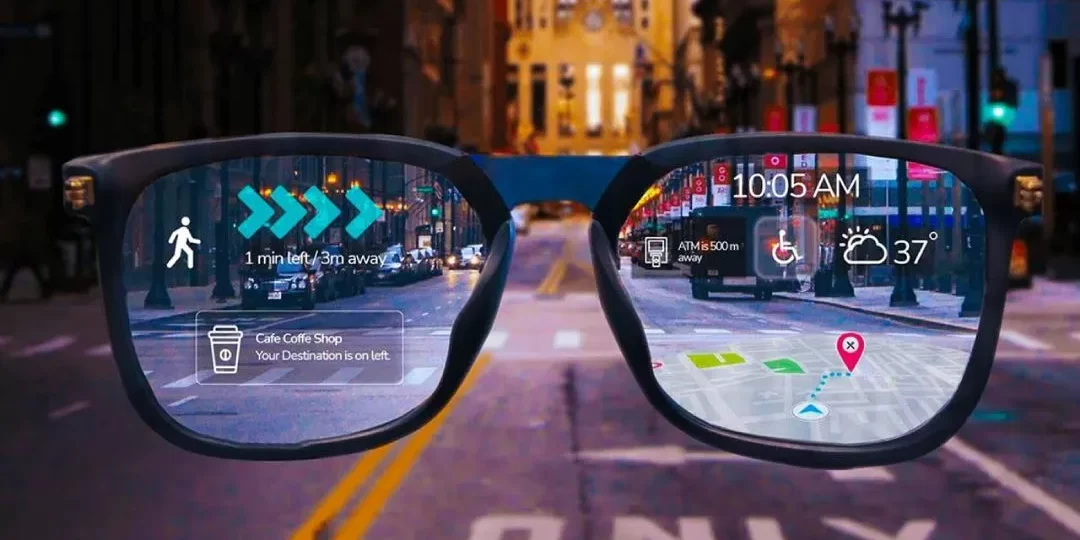
The once-futuristic promise of Augmented reality (AR) is now taking bold strides forward, thanks in large part to advancements in AR smart glasses. These powerful tools are unlocking new layers of interactivity that blend the digital and physical worlds like never before. With interactivity modalities improving rapidly—from voice and gesture controls to contextual information overlays—AR smart glasses are poised to revolutionize industries from healthcare to real estate, manufacturing, and beyond. Here’s a look at how AR smart glasses are evolving and the transformative potential they hold for diverse sectors.
The latest generation of AR smart glasses showcases remarkable improvements in interactivity, opening up innovative possibilities for both consumers and businesses. These interactivity modalities allow users to:
Navigate Information Seamlessly: Smart glasses are evolving to recognize and display relevant information based on contextual awareness. For instance, technicians repairing complex machinery can access digital schematics or tutorials projected onto their field of view as they work, with minimal input needed.
Engage Hands-Free with Voice and Gesture Controls: Voice recognition and gesture tracking have progressed to enable natural, intuitive ways of controlling AR displays. This is especially valuable in environments where hands-free operation is critical, such as healthcare or construction.
Leverage Real-Time Data with Immediate Feedback: AR smart glasses can now provide real-time feedback through connected sensors and AI. Imagine field workers seeing live feedback on maintenance tasks or warehouse workers getting alerts on safety protocols or stock data—displayed right in front of them.
Enhance Collaboration with Remote Interaction: Smart glasses allow users to transmit what they’re seeing to a remote expert or colleague, who can then annotate their view in real time. This interactivity enables effective, remote collaboration, which is crucial in fields requiring expertise from afar, such as emergency services or technical repairs in remote locations.
Industry-Specific Use Cases of AR Smart Glasses
With the advancements in interactivity, AR smart glasses are finding real-world applications that go far beyond initial, niche uses. Here are some of the ways industries are benefiting from this technology:
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, AR smart glasses are reshaping the way professionals approach surgery, diagnosis, and training. Surgeons can now have real-time access to patient data, images, and vital stats directly in their line of sight, reducing the need to look away to check monitors. In operating rooms, AR overlays can guide precise incisions and offer anatomical mapping, allowing for safer and more efficient procedures. Beyond surgeries, AR glasses are being used in medical training to simulate patient interactions or complex procedures, offering a hands-on learning experience without risk.
2. Manufacturing and Field Service
In manufacturing, AR smart glasses enhance productivity and reduce error rates by providing step-by-step guidance to workers assembling intricate machinery or performing quality checks. Maintenance technicians can pull up blueprints, 3D models, and troubleshooting guides as they work, making repairs faster and more accurate. Moreover, remote experts can guide field workers in real-time, addressing issues in oil rigs, construction sites, or remote wind farms, where expertise might not be readily available.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Retailers are exploring AR smart glasses to elevate the customer experience. Sales associates equipped with AR glasses can access product details, inventory data, and customer preferences on the go, helping them provide personalized service. In e-commerce, AR is transforming how customers interact with products: virtual try-ons allow shoppers to see how items like glasses, clothing, or makeup look on them in real-time, bridging the gap between online and in-store experiences.
4. Real Estate and Architecture
AR smart glasses are becoming invaluable tools in real estate, architecture, and interior design. Real estate agents can use AR glasses to provide virtual tours, allowing clients to visualize spaces with customizations like color schemes, furniture layouts, or structural modifications. Architects and builders, too, can use AR overlays to visualize projects at various stages, ensuring design intent matches reality and reducing costly changes in the construction phase.
5. Logistics and Warehousing
For logistics, AR smart glasses streamline warehouse operations by providing workers with optimized picking routes, inventory details, and order updates directly in their line of sight. This boosts efficiency by guiding workers through warehouses, showing them where items are located, and verifying correct picks—all without having to rely on handheld devices. In warehousing, AR glasses can also display real-time data, keeping teams informed about stock levels, delivery timelines, and restocking priorities.
Challenges and Opportunities
While AR smart glasses hold immense potential, they still face technological and societal challenges. Privacy concerns, data security, and social acceptance remain crucial hurdles to overcome. Additionally, challenges in miniaturizing hardware, extending battery life, and developing seamless user interfaces persist. However, with continued investment and innovation, these obstacles are likely to diminish over time.
The Role of AI in Enhancing AR Glass Interactivity
One of the most promising areas for improvement in AR smart glasses is integrating artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance interactivity. AI-powered natural language processing, for instance, can refine voice commands to make glasses responsive in noisy or complex environments. Similarly, AI can be used to make sense of contextual data and deliver insights precisely when and where they’re needed.
Expanding Accessibility and Affordability
As the technology becomes more widespread, we can expect AR glasses to become more affordable and accessible. This could democratize access to AR-powered training, assistive technology, and remote support across multiple industries, from startups and smaller companies to NGOs operating in remote areas.
Conclusion: A New Reality with Infinite Possibilities
As AR smart glasses continue to evolve, the line between digital and physical experiences will blur further, creating a reality where valuable information, interactivity, and experiences are seamlessly integrated into our everyday world. Whether through hands-free medical guidance, immersive retail experiences, real-time maintenance support, or transforming how we envision architecture, AR smart glasses are a testament to how technology can redefine industries, enhance productivity, and bring people closer—even if separated by miles.
In the not-so-distant future, AR smart glasses may become as ubiquitous as smartphones, ushering in a new era of interactive possibilities. As they continue to advance, one thing is certain: we’re only beginning to unlock their potential. The challenge now lies not just in technological development but in the creative and responsible application of this technology across industries to shape a future where AR enhances, rather than disrupts, our lives.